We Look forward to Helping YOU!
Focus on Shin Splints
What is it?
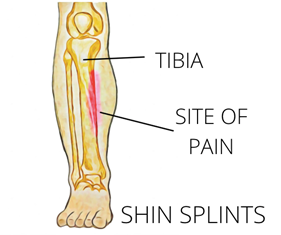
Shin splints, are a painful condition of the lower leg, also known as Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome, it is an overuse injury that causes pain along the inside of the tibia or shin bone. It is a common condition in runners, hikers and soldiers who march long distances.
What are the symptoms?
Shin splints are typified by persistent leg pain, usually the inside of the shin, halfway down the lower leg. The pain might be felt during exercise or directly after. Some people experience a dull ache over their shin that lasts for quite a while after exercise stops, while for others the pain may be sharp and fade quickly. The pain is often progressive, becoming worse with shorter distances. Eventually, shin splints can severely impact activity levels as the pain becomes too severe to continue exercising.
Shin splints can be extremely painful and very disruptive to activity levels. As the pain usually starts gradually and progresses many people find themselves unable to continue training, shin splints may also progress to stress fractures if not diagnosed early and managed effectively.
Shin splints are typified by persistent leg pain, usually the inside of the shin, halfway down the lower leg. The pain might be felt during exercise or directly after. Some people experience a dull ache over their shin that lasts for quite a while after exercise stops, while for others the pain may be sharp and fade quickly. The pain is often progressive, becoming worse with shorter distances. Eventually, shin splints can severely impact activity levels as the pain becomes too severe to continue exercising.
How does it happen?
Shin splints are predominantly seen in runners who increase their distances quickly, often while training for an event. Activities that require repetitive weight-bearing of any kind, such as marching or high impact sports have also been shown to cause shin splints. Although the pathology of shin splints is unclear, studies have been able to identify certain risk factors that may predispose someone to shin splints. These include;
- An abrupt increase in activity level
- Improper footwear and support
- Higher BMI
- Training on hard or uneven surfaces
- Tight calf muscles
- Flat feet
- Increased external rotation range of the hips
- Females are more likely to develop shin splints than males.
- Prior history of shin splints
- Wearing or having worn orthotics
How can physiotherapy help?
The first step for your physiotherapist will be to address any contributing factors and help to adapt your training program to a level that is optimum for you. A period of relative rest may be recommended along with a targeted strengthening and stretching program for any tight or weak muscles. Switching to low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling and yoga may also help to maintain fitness during recovery. Your running technique will be analyzed and any training errors may be corrected. When getting back into your training routine, it is usually recommended that distances are not increased by more than 10% per week as this allows the tissues of the body to react to the increased demands and adapt accordingly.
None of the information in this newsletter is a replacement for proper medical advice. Always see a medical professional for advice on your injury.
Shin splints can be extremely painful and very disruptive to activity levels. As the pain usually starts gradually and progresses many people find themselves unable to continue training, shin splints may also progress to stress fractures if not diagnosed early and managed effectively.
How does it happen?
Shin splints are predominantly seen in runners who increase their distances quickly, often while training for an event. Activities that require repetitive weight-bearing of any kind, such as marching or high impact sports have also been shown to cause shin splints. Although the pathology of shin splints is unclear, studies have been able to identify certain risk factors that may predispose someone to shin splints. These include;
- An abrupt increase in activity level
- Improper footwear and support
- Higher BMI
- Training on hard or uneven surfaces
- Tight calf muscles
- Flat feet
- Increased external rotation range of the hips
- Females are more likely to develop shin splints than males.
- Prior history of shin splints
- Wearing or having worn orthotics
How can physiotherapy help?
The first step for your physiotherapist will be to address any contributing factors and help to adapt your training program to a level that is optimum for you. A period of relative rest may be recommended along with a targeted strengthening and stretching program for any tight or weak muscles. Switching to low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling and yoga may also help to maintain fitness during recovery. Your running technique will be analyzed and any training errors may be corrected. When getting back into your training routine, it is usually recommended that distances are not increased by more than 10% per week as this allows the tissues of the body to react to the increased demands and adapt accordingly.
None of the information in this newsletter is a replacement for proper medical advice. Always see a medical professional for advice on your injury.






Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
 Write your caption hereButton
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

-

-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton 
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
 Button
Button
-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Opening Hours
- Monday
- -
- Tuesday
- -
- Wednesday
- -
- Thursday
- -
- Friday
- -
- Saturday
- -
- Sunday
- Closed
Additional Specialties
Acupuncturist
Clinical Pilates & Group Exercise
Women's Health & Pregnancy Care
Paediatric (Children's) Physiotherapy
Art Therapy
Counsellor
Psychologist