We Look forward to Helping YOU!
Should You Have a Joint Replacement?

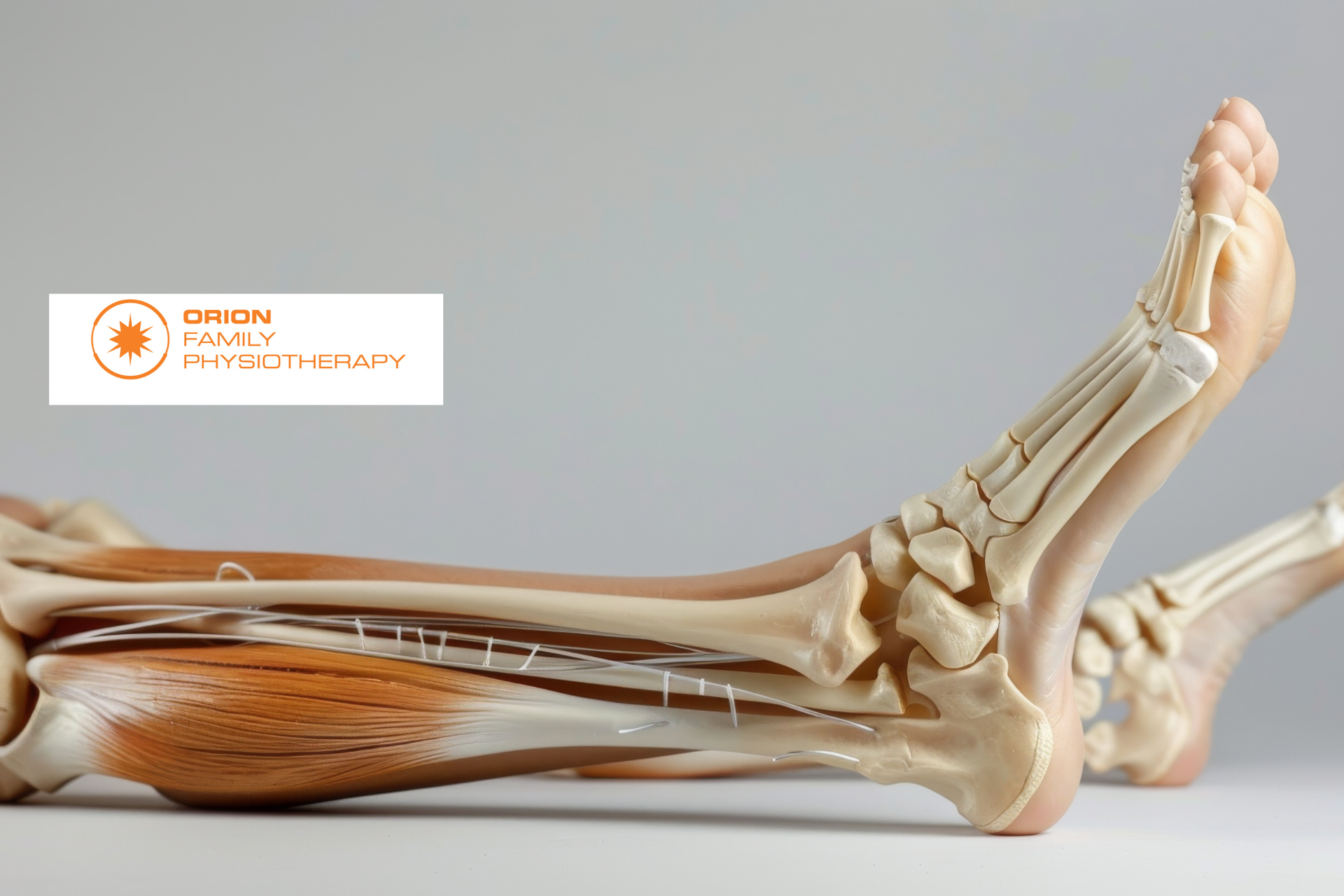
One of the most impressive healthcare developments in history is the humble joint replacement. Many people are able to take a joint that is extremely painful and dysfunctional and give it a whole new lease on life.
The improvements in this surgery over the last few decades have meant that success rates for joint replacement surgery, particularly hip and knee replacements are even higher than ever. If you are struggling with joint pain related to arthritis, it can be difficult to know when to make the move. Here are a few things to consider before going for that surgical consult.
Don't assume pain is permanent once you hear the word arthritis
Pain is a complex beast and is usually never caused by one single thing. Most people will have some amount of arthritis in their joints past the age of 50, whether or not this is what is causing your pain will be unclear without first seeking physiotherapy treatment.
Many people have some level of degeneration in their joints without experiencing much discomfort at all. It's possible that an analysis of biomechanics, strengthening and manual therapy could all improve your symptoms significantly, even if osteoarthritis is present.
A trial of physiotherapy treatment is recommended before surgery in most cases.
Pre-surgical strength and fitness are important
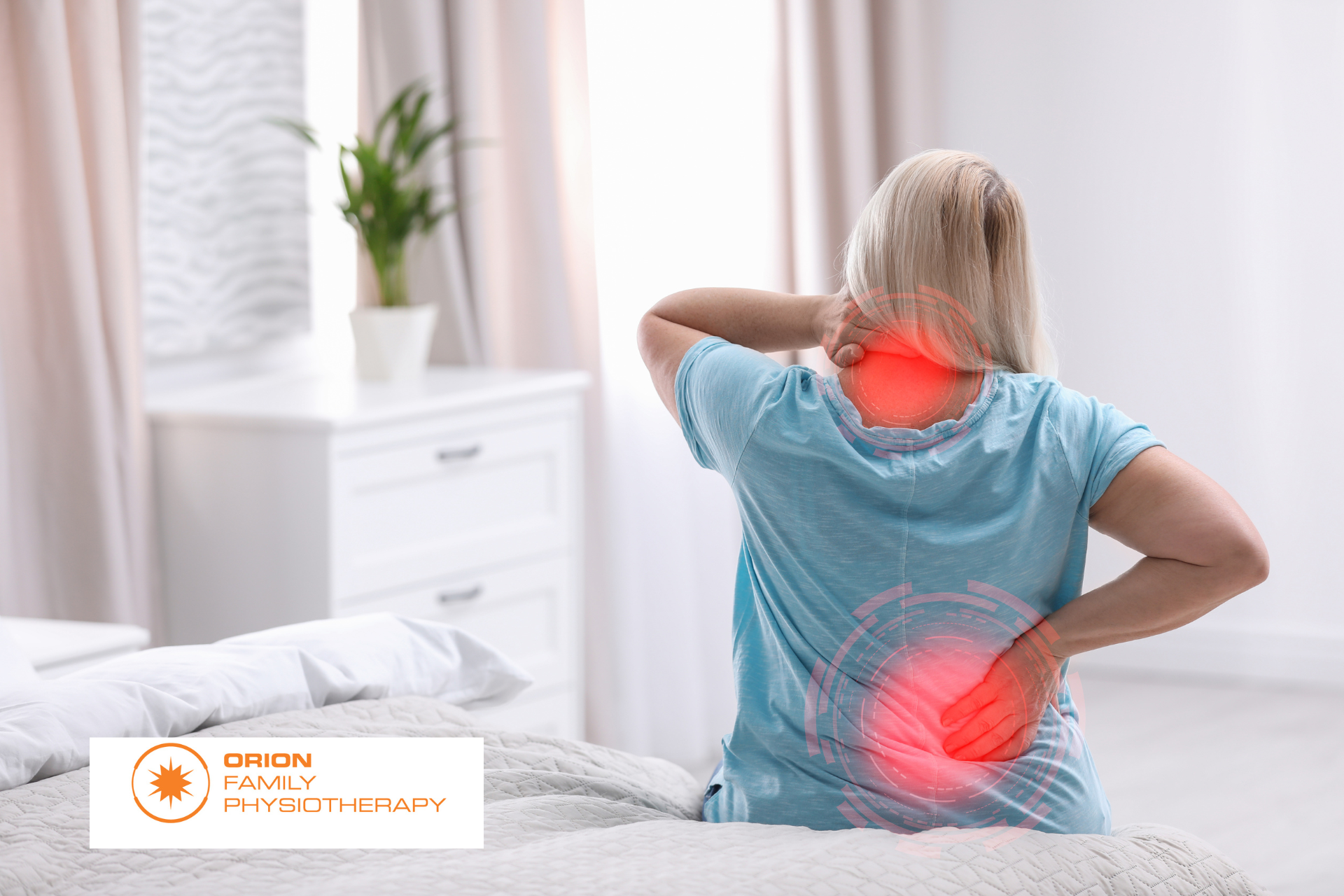
This means two things, first of all, your strength or exercise program before surgery will set you up for much better results. The second thing is that choosing when to have the surgery means not necessarily waiting until the pain is unbearable before going ahead, as time spent in significant pain can reduce your overall strength and fitness while also putting more stress on other joints.
Research the risks and side effects
While surgical outcomes are continually improving, no surgery comes without risks and some people will have ongoing pain and stiffness even after their surgery. It is important to make an informed decision about when and if you should have a joint replacement.
If you are considering a joint replacement, speak to your physiotherapist about all the ways they can support you through your journey and help you come to an informed decision about what is right for you.
None of the information in this article is a replacement for proper medical advice. Always see a medical professional for advice on your individual injury.





Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
 Write your caption hereButton
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

-

-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton 
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
 Button
Button
-

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton -

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Opening Hours
- Monday
- -
- Tuesday
- -
- Wednesday
- -
- Thursday
- -
- Friday
- -
- Saturday
- -
- Sunday
- Closed
Additional Specialties
Acupuncturist
Clinical Pilates & Group Exercise
Women's Health & Pregnancy Care
Paediatric (Children's) Physiotherapy
Art Therapy
Counsellor
Psychologist